beginner
In the world of finance and investment, understanding the true value of an asset, especially that of a company, is crucial. This value is often reflected in “book value”, which provides insight into the net value of a company’s assets, subtracting the liabilities. It offers a concrete, quantifiable metric that reflects the worth of a company according to its financial statements.
Diving deeper into the calculation of book value gives investors a clearer picture of a company’s financial health and aids in making informed investment decisions. This article will talk about what book value is, how it is calculated, provide the book value formula, and, as always, look at this financial analysis tool from the crypto perspective.
What Is Book Value? The Definition
Book Value represents the value of a company as recorded on its balance sheet. It’s essentially the difference between a company’s total assets and total liabilities. In other words, if a company were to liquidate all its assets and pay off all its debts, the book value would represent the capital that remains for the common stockholders.
This value, often derived from financial statements, is based on the original cost of the asset minus any accumulated depreciation or amortization, without adjustments for inflation or the assets’ current market value. It’s crucial to note that book value incorporates tangible assets (like real estate and machinery) but might exclude intangible assets (like copyrights or patents) unless they have a historical cost associated with purchase.
How to Calculate Book Value
To determine the book value of a company:
- Begin by identifying the company’s total assets and total liabilities from its balance sheet.
- Subtract the total liabilities from the total assets.
Therefore, the book value formula is: Book Value = Total Assets − Total Liabilities
This resulting figure gives you the net value of the company’s assets over time.
Book Value vs. Market Value
While book value is derived from the balance sheet based on historical cost, market value represents the current value of an asset or company in the marketplace. In the context of a publicly traded company, market value can be determined by multiplying its current share prices by the number of outstanding shares. Often, there’s a discrepancy between a company’s book value and market price due to factors like growth expectations, intangible assets, and the subjective nature of how investors perceive a company’s future prospects.
Price-to-Book (P/B) Ratio
The Price-to-Book ratio compares a company’s market price to its book value. It’s calculated as:

A P/B ratio of less than 1 can indicate an undervalued stock or negative market sentiments, whereas a ratio greater than 1 might suggest the opposite. However, investment decisions should not rely solely on this metric, as it doesn’t capture the whole financial scenario of a company.
Book Value per Share (BVPS)
BVPS is a measure to determine the book value attributed to each outstanding share of common stock. It’s computed by dividing the company’s book value by the number of common shares.
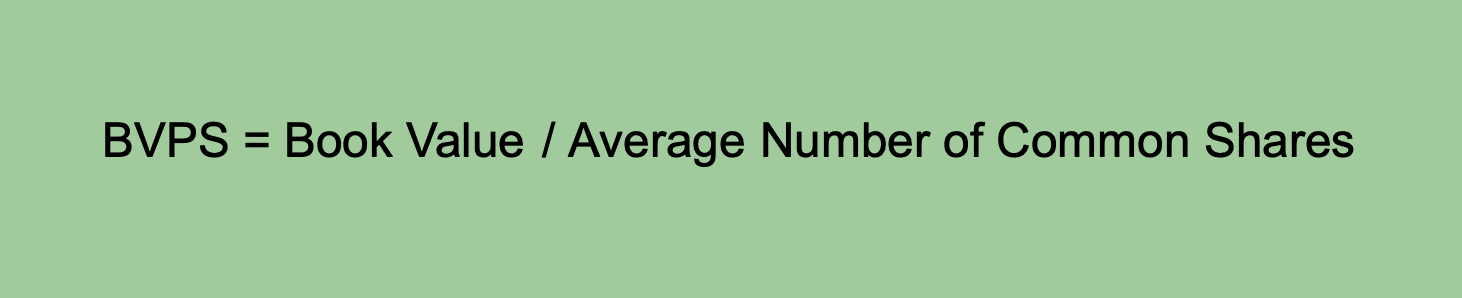
It’s a useful metric for investors to assess the price per share and evaluate the fairness of the current share prices against the value represented on the balance sheet.
Mark to Market Valuation
Mark to Market (MtM) valuation is a method where assets and liabilities get valued at their current market prices rather than historical costs. This approach provides a more real-time assessment of an asset’s value, unlike the traditional book value which relies on the original cost. Especially in industries with high volatility in asset prices, MtM provides more clarity on real-time asset value.
Example of Using Book Value
Consider a hypothetical company, XYZ. From its financial statements, we note that:
- Total Assets: $8 million (of which $2 million are intangible assets)
- Total Liabilities: $4 million
- Outstanding common shares: 1 million
To calculate the book value: $8 million – $4 million = $4 million
However, if we consider only tangible assets, the tangible book value would be $4M – $2M = $2M.
Next, the BVPS (Book Value of Equity per Share): $4M / 1M shares = $4 (stock prices per share).
If the current market price of EstateLand Inc.’s stock is $8, the P/B ratio would be: $8/ $4 = 2
This means the stock is trading at twice its book value, which can be a subject of evaluation for potential investors looking into the real estate sector.
Book Value and Cryptocurrency
Cryptocurrency, by its very nature, challenges the traditional financial system, and book value is no exception. Traditional assets and companies have tangible and intangible assets on their balance sheets, which allows investors to perform the calculation of book value.
Cryptocurrencies, on the other hand, do not possess tangible assets in the traditional sense, making the concept of book value somewhat nebulous in the crypto space. There isn’t a balance sheet for Bitcoin or Ethereum, with physical or capital assets and liabilities that can be easily quantified.
However, when it comes to cryptocurrency projects or companies that hold vast amounts of digital assets or are involved in the broader blockchain ecosystem, the concept of book value might find some relevance. Crypto investors can examine the balance sheets of these companies to determine the book value of the firm’s total cryptocurrency holdings and assets by subtracting liabilities.
This could offer a glimpse into whether the company’s market value (reflected in its market capitalization, stock or token price) aligns with its net asset value, potentially highlighting undervalued investment opportunities. While the direct application of the book value metric might not fit the decentralized ethos of cryptocurrencies, it still holds value in the broader landscape where traditional finance intersects with the crypto world.
FAQ
Why is market value often higher than book value?
Market value often exceeds book value because it encompasses a broader range of factors than the strict accounting value reflected on a company’s balance sheet. While book value, sometimes referred to as carrying value, is grounded in the historical cost basis of an asset, market value considers the fair market value and the perceived value of the asset’s market potential.
This perception can be influenced by aspects such as the company’s earnings growth, earnings potential, and the values of assets like intangible assets, which might not be fully captured in the book value. Additionally, market values can be swayed by the sentiments and expectations of investors over periods of time, leading them to value individual shares at a premium compared to their book value.
What’s a good P/B ratio?
A good Price-to-Book (P/B) ratio is relative and can vary by industry, but in general, a P/B ratio below 1 might indicate that the stock is undervalued or that the market has a pessimistic view regarding the company’s future prospects. Conversely, a higher P/B ratio could suggest that the stock is overvalued or that investors have high expectations for the company’s earnings growth and earnings potential. Value investors, particularly, often seek stocks with lower P/B ratios as potential investments, believing they’re buying at less than the fair market value.
How can I use book value?
Book value is a useful metric for investors and business owners to evaluate a company’s net value, providing insights into its financial health and stability. Investors can compare the book value and the market value of individual shares to understand if a stock is undervalued or overvalued. A significant difference between these values might indicate market inefficiencies or insights into the company’s future potential.
Additionally, comparing the book values of companies within the same industry can help in identifying better investment opportunities. Business owners can use book value as a benchmark for asset valuation, ensuring they have an accurate understanding of their company’s worth, especially when considering sales or mergers.
Why is it called “book value”?
The term “book value” originates from the accounting practice of recording an asset’s value in the company’s “books” or financial statements.
What is net book value?
Net book value is another way to refer to book value.
Disclaimer: Please note that the contents of this article are not financial or investing advice. The information provided in this article is the author’s opinion only and should not be considered as offering trading or investing recommendations. We do not make any warranties about the completeness, reliability and accuracy of this information. The cryptocurrency market suffers from high volatility and occasional arbitrary movements. Any investor, trader, or regular crypto users should research multiple viewpoints and be familiar with all local regulations before committing to an investment.


