beginner
Recently, decentralized applications (dApps) have become more widely used due to their potential to transform digital interactions.
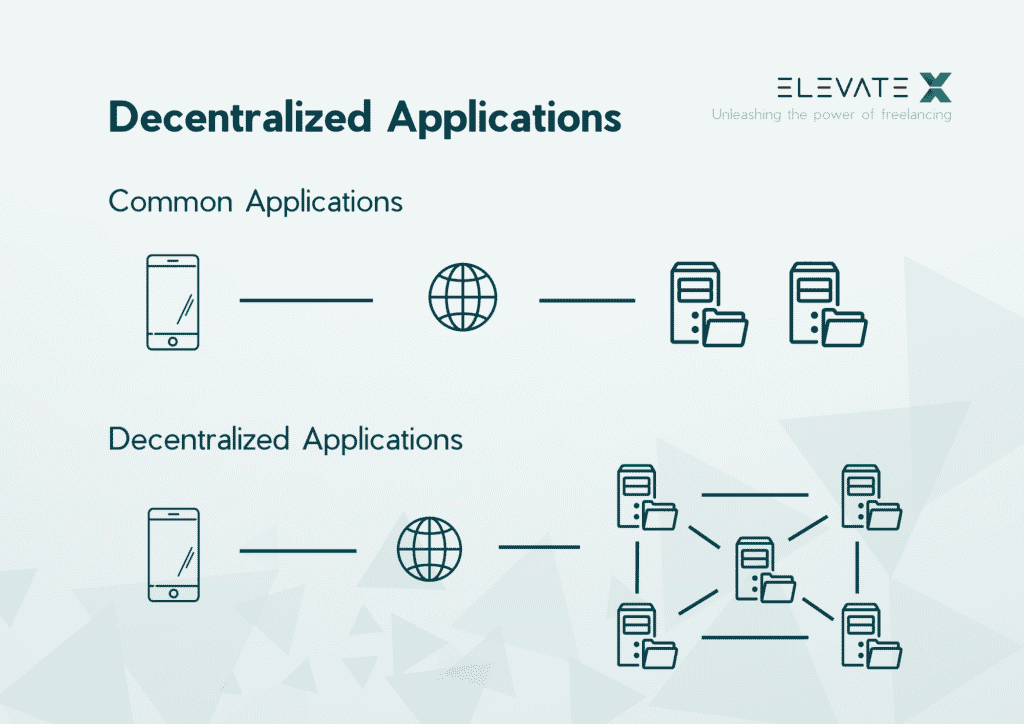
In the conventional app ecosystem, control over user experience and data is typically managed by centralized entities such as app stores or platform providers. DApps, however, offer users more power as they are based on decentralized infrastructures that are not managed by any particular entity.
This article outlines dApps, the way they work, and their future potential. What do you think? Will decentralized applications be able to revolutionize different industries?
What are Decentralized Applications (dApps)?
According to their definition, dApps are applications that run on decentralized networks, such as blockchains or peer-to-peer networks, without a centralized authority’s maintenance or control. The popularity of dApps can be attributed to their capacity to provide a transparent, secure, and equitable system in comparison with centralized applications. DApps differ from traditional apps in that they are not run by a single entity, giving users more control over their data and digital assets.
DApps are a promising and innovative technology with the potential to transform various industries and sectors, including but not limited to finance, healthcare, and logistics.
What Makes DApps Different? DApps vs. Traditional Apps
There are several key differences between dApps and traditional apps.
Decentralized architecture
DApps are software applications that don’t rely on a centralized entity, thanks to their decentralized nature. Meanwhile, traditional apps are typically managed by one entity, such as an app store or a platform provider.
Transparency
Decentralized applications are based on a public ledger that makes all data and transactions transparent and hard to alter. Traditional apps, on the other hand, typically do not provide users with information on how their data is being managed.
Security
Apps running on a decentralized network have an advantage in terms of security, as they are less vulnerable to cyber threats due to the lack of single-point failure. In contrast, traditional apps are more prone to security issues.
Autonomy
Decentralized apps can operate independently, without intermediaries, which decreases transaction costs and speeds up the transaction process. Traditional apps often operate with the help of intermediaries, such as banks or other financial institutions, which can slow down the transaction process and increase costs.
DApp Examples
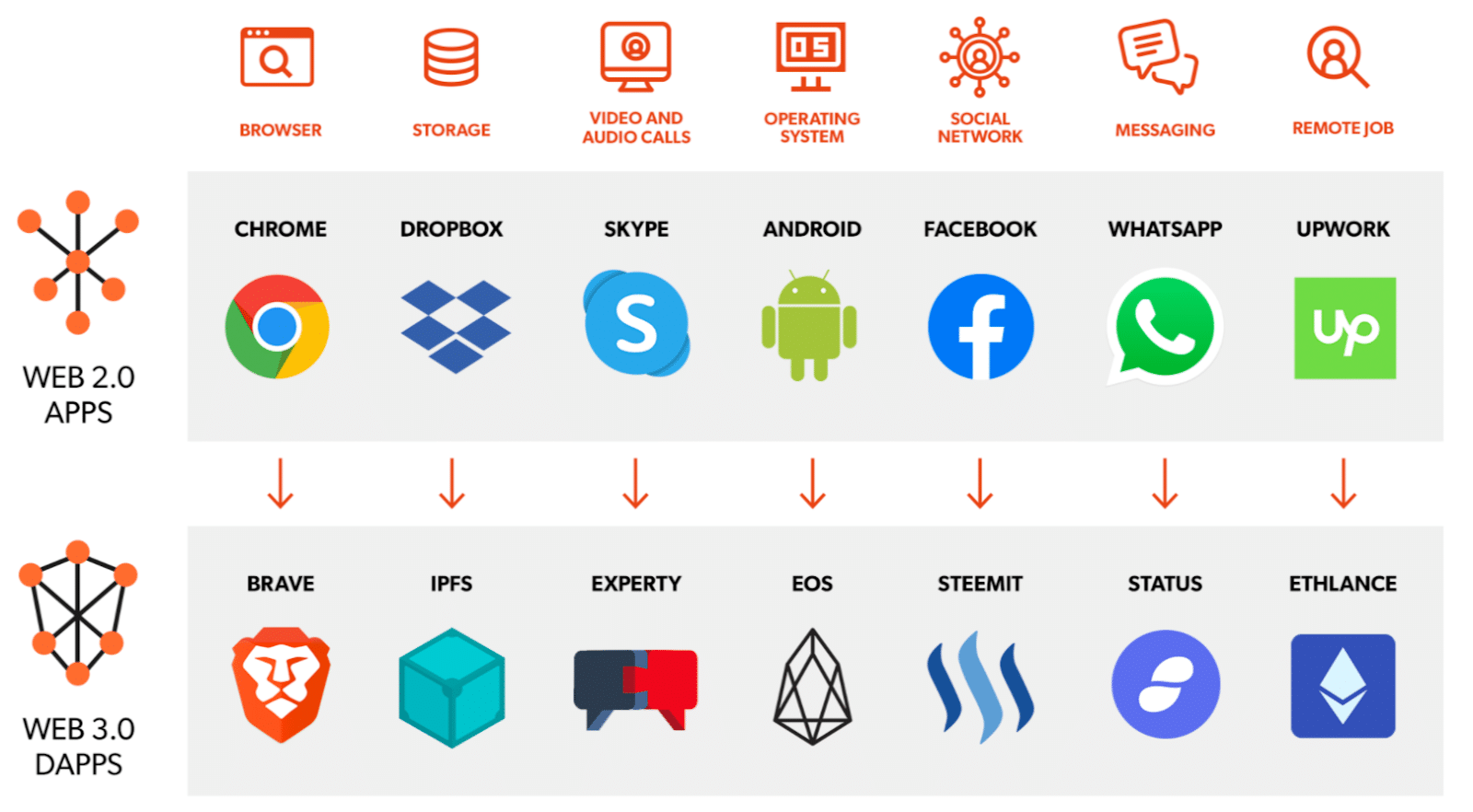
There are many different decentralized applications on various blockchain networks. The most popular platforms for dApps are the Ethereum network and Tron. According to the website DappRadar, most of the biggest decentralized apps also belong to the DeFi (decentralized finance) category, with some gaming dApps and decentralized exchanges sprinkled in.
One such popular DEX is Uniswap, a decentralized exchange that enables users to trade cryptocurrencies without intermediaries. Besides, customers don’t have to rely on a centralized server. Decentralization offers Uniswap users more control over their digital assets, as well as lower transaction fees and faster transaction times than centralized exchanges.

Another popular dApp is Brave Browser, a decentralized browser providing users with enhanced privacy and security through ad and tracker blocking. Brave Browser empowers users to manage their own online privacy and data through decentralization, as opposed to relying on centralized parties to protect personal information.
How Do DApps Work?
DApps are decentralized applications built on decentralized blockchain networks and run without central authorities. They rely on decentralized networks, smart contracts, tokens, user interfaces, and consensus mechanisms to provide secure, transparent, and efficient interactions with digital technology.
Decentralized network
DApps are applications that run on a network of distributed computers instead of a single server. This network is typically a blockchain, which is a decentralized database that stores data and transactions across its network of nodes.
Tokens
DApps often use tokens, which are digital representations of value, such as cryptocurrency or virtual assets. Tokens can be held on a blockchain and transferred between users as a form of payment or ownership.
Consensus
In a network with decentralized architecture, consensus ensures the validity and security of all transactions and data. Various consensus mechanisms, such as Proof of Work and Proof of Stake, can be used to reach a consensus.
Smart contracts
DApps usually incorporate smart contracts — digital agreements which are held on the blockchain and can be executed autonomously when predetermined conditions are fulfilled. Smart contracts allow dApps to function autonomously, creating a more secure and transparent digital experience for users.
Many dApps rely on smart contracts to automate certain functions and transactions. A decentralized exchange (DEX) dApp can utilize smart contract technology to facilitate trades between buyers and sellers without involving a central governing body. A DeFi dApp can utilize a smart contract to enable lending and borrowing between users without the involvement of a central authority.
The Challenges and Limitations of DApps
While dApps offer many benefits, such as transparency, security, and autonomy, they also face several challenges and limitations.
- Scalability. Scalability is a major challenge for dApps. As the usage of dApps increases, the network can become slower and congested. This can result in slower transaction times and higher fees, which can make it difficult for dApps to scale and promote adoption.
- User Experience. One of the challenges faced by dApps is the ease of use. DApps are typically based on decentralized networks. This often goes hand in hand with complex user interfaces that require specific technical knowledge from users. As a result, mainstream users may find it challenging to adopt and utilize dApps.
- Interoperability. Interoperability can be an issue with dApps running on different blockchains or using different standards. This can limit their functionality and usefulness.
- Regulation. The adoption and development of dApps may be hindered due to regulatory uncertainty. Regulators may be unsure of how to categorize dApps, what taxes may be applied to them, and the extent of regulation that should be enforced.
The Future of DApps
So far, the crypto community is cautiously optimistic about the future of dApps. Decentralized apps have much potential to become the driving force behind crypto’s journey to the mainstream. Of course, there are still quite a few challenges to overcome, like the ones we listed above. However, the future of dApps still looks pretty bright.
There’s a lot of research involved in the scene. As it is a new niche with high profitability margins, it naturally attracts many entrepreneurs and talented professionals, which shows good promise for all the aforementioned challenges to be eventually solved.
Research and development are carried out to enhance the scalability and user experience of dApps. The implementation of these improvements will make dApps simpler to use and easier for mainstream users to access.
There are many potential applications for dApps, and their range is expanding. Each decentralized application provides an alternative means of interacting with digital technology that is decentralized, transparent, and secure across a range of industries, including finance, gaming, and supply chain management. As more use cases are developed and proven successful, more users will be drawn to dApps.
Decentralized Finance
DApps and decentralized finance are incredibly interconnected. As the popularity of DeFi grows, so do the use cases for decentralized applications, like a decentralized credit service or an exchange platform.
DeFi provides a new approach to interacting with financial services. Demand for decentralized financial systems is increasing as traditional financial systems and centralized apps receive more scrutiny and criticism due to the desire for greater autonomy and transparency.
FAQ
What are dApps used for?
A decentralized app can be used for anything that can benefit from the transparency and security it provides. Currently, dApps mainly find their application in DeFi, where they enable users to make financial transactions without intermediaries.
How are dApps different from normal apps?
Unlike apps running on centralized servers, dApps use decentralized networks like the Ethereum blockchain. This allows them to drop middlemen and provide a more trustless and secure way to handle user data and transactions.
What can you use to interact with dApps?
This depends on the type of dApp you’re using. Web browsers, games, exchanges, and so on can usually be accessed like any traditional app. Some dApps, however, aren’t as easy to use. In any case, you will most likely need to have a crypto wallet that can be connected to those platforms, like MetaMask.
How can you create a dApp?
Creating a dApp is no easy process. First, you will need to choose a platform — the Ethereum network, EOS, and Tron are the most popular ones. Next, define your use case and think about the kind of problem your app will solve.
After this, it’s time to start designing and developing your dApp. Make sure your interface is user-friendly, and be careful when writing smart contracts that will govern the behavior of your project. Once you’re done, don’t forget to do extensive tests before deploying your new dApp.
Disclaimer: Please note that the contents of this article are not financial or investing advice. The information provided in this article is the author’s opinion only and should not be considered as offering trading or investing recommendations. We do not make any warranties about the completeness, reliability and accuracy of this information. The cryptocurrency market suffers from high volatility and occasional arbitrary movements. Any investor, trader, or regular crypto users should research multiple viewpoints and be familiar with all local regulations before committing to an investment.

